Mississippi River Initiative
To safeguard the Mississippi River, a comprehensive research project comprising two distinct approaches has been proposed: the SMRT Program and the SMRT Challenge.
-
Location
Mississippi River, USAYear
2023 -
RebelGroup
H+N+S
Deltares -
Embassy of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the USA
Mississippi River Cities and Towns Initiative
Andrew J. Young Foundation -
Design lead
Rens WijnakkerProject lead
Rens WijnakkerTeam members
Mark Slierings
Arina Novikova
“The Mississippi River stands as one of the world’s largest rivers, playing a critical role as a vital artery for global and national interests, such as commerce, transportation, agriculture, energy, manufacturing, and nature conservation.”
— Rens Wijnakker
Strategic investments
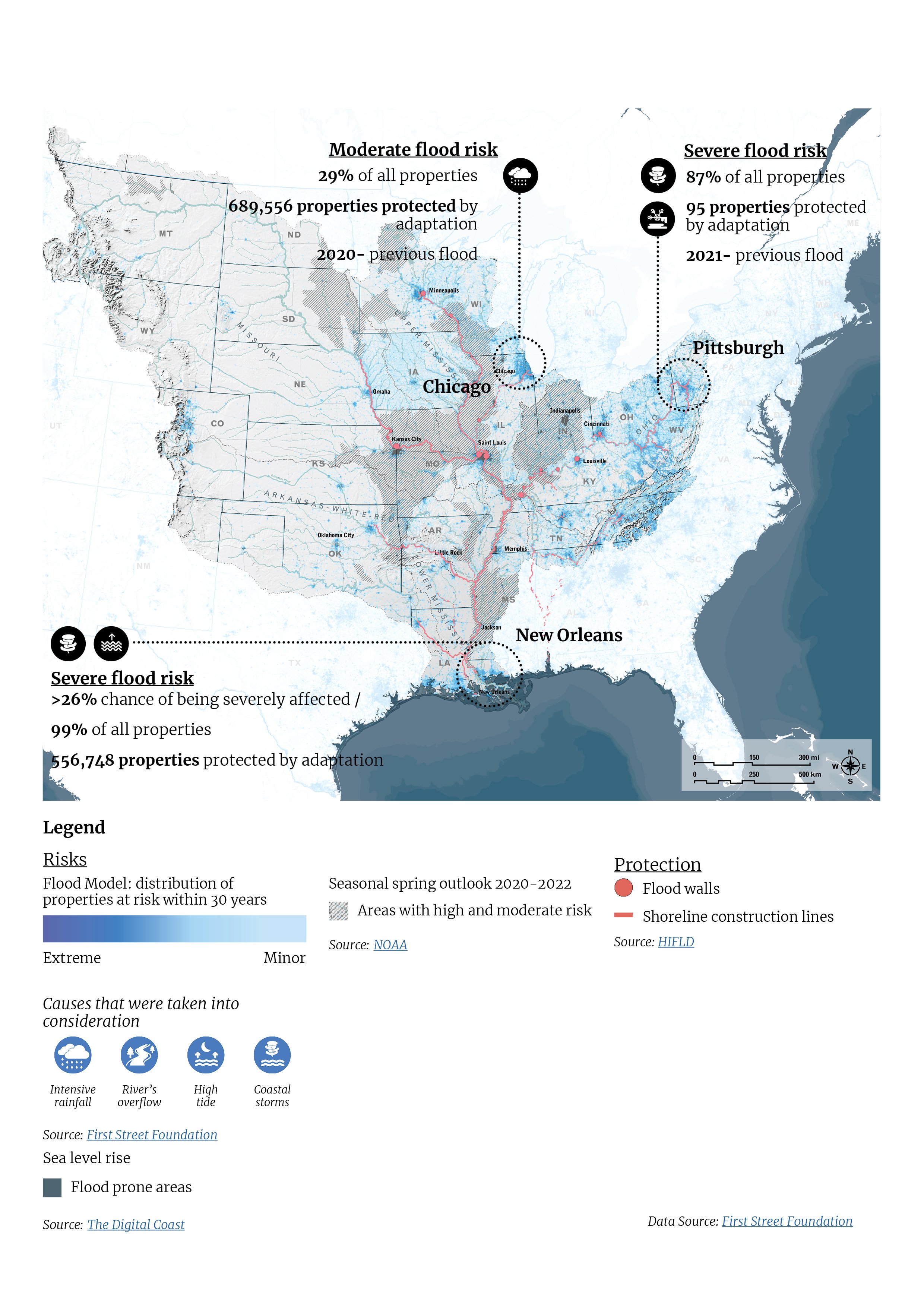
The Mississippi River stands as one of the world’s largest rivers, playing a critical role as a vital artery for global and national interests, such as commerce, transportation, agriculture, energy, manufacturing, and nature conservation. However, the river faces mounting challenges, including flooding, droughts, and water quality issues, all of which threaten its sustainability.
To safeguard the Mississippi River, a comprehensive research project comprising two distinct approaches has been proposed: the SMRT Program and the SMRT Challenge. The Challenge aims to generate new funding and financing solutions, amounting to $60 billion, to address the pressing issues plaguing the river. Rather than viewing improvement projects as mere ‘cost centers’, the focus is on considering them as strategic investments in economic development, catalysing positive impacts on social and environmental aspects.
Meanwhile, the SMRT Program will coordinate research, monitoring, and planning efforts to ensure the sustainable development of the entire Mississippi River system, with an emphasis on natural solutions and ecological restoration. The Program revolves around six primary goals, encompassing water management, social equity, environmental preservation, and economic growth.
The SMRT Program and SMRT Challenge are both scheduled to commence later this year.
Goals
-
Living with floods
The Mississippi River is prone to floods due to its expansive watershed and unpredictable weather patterns. Factors such as land use changes, urbanization, and deforestation can worsenthe impact of floods. Climate change has also contributed to an increase in the frequency and intensity of floods.
-
Coping with droughts
Droughts are another challenge faced by the Mississippi River watershed. Climate change has led to more frequent and severe droughts in the region. Droughts can result in low water levels, reduced river flows, decreased agricultural productivity and decreased ship loading capacity.
-
Ensuring water quality
The Mississippi River is one of the most polluted rivers in the United States, mainly due to agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and urbanization. The pollution can harm aquatic life, degrade water quality, and affect human health.
-
Enhancing social inclusion and equity
The communities living in the Mississippi River watershed face several challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, poverty, and social inequality. Additionally, the river’s floods and droughts can pose significant risks to public safety and health. Improving infrastructure, enhancing social inclusion, and ensuring equitable access to resources can improve the liveability of the region.
-
Restoring ecosystems
The Mississippi River watershed is home to diverse ecosystems and habitats, such as wetlands, forests, and prairies. Human activities have caused significant damage to these ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, biodiversity decline, and ecosystem collapse. Restoration efforts are necessary to preserve the natural heritage of the region.
-
Stimulating economical growth
The Mississippi River is a critical economic asset, providing a transportation artery for goods and commodities. However, economic activities such as agriculture, industry, and shipping have also contributed to the river’s degradation. Balancing economic growth with sustainable resource use and environmental protection is crucial for the long-term economic competitiveness of the region.